This is the multi-page printable view of this section. Click here to print.
Monitoring and usage
- 1: Track user activity with audit logs
- 2: Use Prometheus monitoring
- 3: Configure Slack alerts
- 4: View organization activity
1 - Track user activity with audit logs
Use W&B audit logs to track user activity within your organization and to conform to your enterprise governance requirements. Audit logs are available in JSON format. Refer to Audit log schema.
How to access audit logs depends on your W&B platform deployment type:
| W&B Platform Deployment type | Audit logs access mechanism |
|---|---|
| Dedicated Cloud |
|
| Multi-tenant Cloud | Available for Enterprise plans only. Available only by using the API. |
| Self-Managed | Synced to instance-level bucket every 10 minutes. Also available using the API. |
After fetching audit logs, you can analyze them using tools like Pandas, Amazon Redshift, Google BigQuery, or Microsoft Fabric. Some audit log analysis tools do not support JSON; refer to the documentation for your analysis tool for guidelines and requirements for transforming the JSON-formatted audit logs before analysis.
For more details about the format of the logs, see Audit log schema and Actions.
Audit log retention
- If you require audit logs to be retained for a specific period of time, W&B recommends periodically transferring logs to long-term storage, either using storage buckets or the Audit Logging API.
- If you are subject to the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 (HIPAA), audit logs must be retained for a minimum of 6 years in an environment where they cannot be deleted or modified by any internal or exterrnal actor before the end of the mandatory retention period. For HIPAA-compliant Dedicated Cloud instances with BYOB, you must configure guardrails for your managed storage, including any long-term retention storage.
Before you begin
-
Organization level admins can fetch audit logs. If you receive a
403error, ensure that you or your service account has adequate permission. -
Multi-tenant Cloud: If you are a member of multiple Multi-tenant Cloud organizations, you must configure the Default API organization, which determines where audit logging API calls are routed. Otherwise, you will receive the following error:
user is associated with multiple organizations but no valid org ID found in user infoTo specify your default API organization:
- Click your profile image, then click User Settings.
- For Default API organization, select an organization.
This is not applicable to a service account, which can be a member of only one Multi-tenant Cloud organization.
Fetch audit logs
To fetch audit logs:
-
Determine the correct API endpoint for your instance:
- Self-Managed:
<wandb-platform-url>/admin/audit_logs - Dedicated Cloud:
<instance-name>.wandb.io/admin/audit_logs - Multi-tenant Cloud (Enterprise required):
https://api.wandb.ai/audit_logs
In the following steps, replace
<API-endpoint>with your API endpoint. - Self-Managed:
-
(Optional) Construct query parameters to append to the endpoint. In the following steps, replace `
with the resulting string. anonymize: if the URL includes the parameteranonymize=true, remove any PII. Otherwise, PII is included. Refer to Exclude PII when fetching audit logs. Not supported for Multi-tenant Cloud, where all fields are included, including PII.- Configure the date window of logs to fetch using a combination of
numdaysandstartDate. Each parameter is optional, and they interact.- If neither parameter is included, only today’s logs are fetched.
numDays: An integer indicating the number of days backward fromstartDateto fetch logs. If it is omitted or set to0, logs are fetched forstartDateonly. Multi-tenant Cloud organizations can fetch up to 7 days of audit logs. In other words, if you setnumDays=9, the effective parameter isnumDays=7.startDate: Controls the newest logs to fetch, in the formatstartDate=YYYY-MM-DD. If it is omitted or explicitly set to today’s date, logs are fetched from today tonumDays(up to7for Multi-tenant Cloud).
-
Construct the fully qualified endpoint URL in the format
<API-endpoint>?<parameters>. -
Execute an HTTP
GETrequest on the fully qualified API endpoint using a web browser or a tool like Postman, HTTPie, or cURL.
The API response contains new-line separated JSON objects. Objects will include the fields described in the schema, just like when audit logs are synced to an instance-level bucket. In those cases, the audit logs are located in the /wandb-audit-logs directory in your bucket.
Use basic authentication
To use basic authentication with your API key to access the audit logs API, set the HTTP request’s Authorization header to the string Basic followed by a space, then the base-64 encoded string in the format username:API-KEY. In other words, replace the username and API key with your values separated with a : character, then base-64-encode the result. For example, to authorize as demo:p@55w0rd, the header should be Authorization: Basic ZGVtbzpwQDU1dzByZA==.
Exclude PII when fetching audit logs
For Self-Managed and Dedicated Cloud, a W&B organization or instance admin can exclude PII when fetching audit logs. For Multi-tenant Cloud, the API endpoint always returns relevant fields for audit logs, including PII. This is not configurable.
To exclude PII, pass the anonymize=true URL parameter. For example, if your W&B instance URL is https://mycompany.wandb.io and you would like to get audit logs for user activity within the last week and exclude PII, use an API endpoint like:
https://mycompany.wandb.io/admin/audit_logs?anonymize=true&<additional-parameters>.
Audit log schema
This table shows all keys which may appear in an audit log entry, ordered alphabetically. Depending on the action and the circumstances, a specific log entry may include only a subset of the possible fields.
| Key | Definition |
|---|---|
action |
The action of the event. |
actor_email |
The email address of the user that initiated the action, if applicable. |
actor_ip |
The IP address of the user that initiated the action. |
actor_user_id |
The ID of the logged-in user who performed the action, if applicable. |
artifact_asset |
The artifact ID associated with the action, if applicable. |
artifact_digest |
The artifact digest associated with the action, if applicable. |
artifact_qualified_name |
The full name of the artifact associated with the action, if applicable. |
artifact_sequence_asset |
The artifact sequence ID associated with the action, if applicable. |
cli_version |
The version of the Python SDK that initiated the action, if applicable. |
entity_asset |
The entity or team ID associated with the action, if applicable. |
entity_name |
The entity or team name associated with the action, if applicable. |
project_asset |
The project associated with the action, if applicable. |
project_name |
The name of the project associated with the action, if applicable. |
report_asset |
The report ID associated with the action, if applicable. |
report_name |
The name of the report associated with the action, if applicable. |
response_code |
The HTTP response code for the action, if applicable. |
timestamp |
The time of the event in RFC3339 format. For example, 2023-01-23T12:34:56Z represents January 23, 2023 at 12:34:56 UTC. |
user_asset |
The user asset the action impacts (rather than the user performing the action), if applicable. |
user_email |
The email address of the user the action impacts (rather than the email address of the user performing the action), if applicable. |
Personally identifiable information (PII)
Personally identifiable information (PII), such as email addresses and the names of projects, teams, and reports, is available only using the API endpoint option.
- For Self-Managed and Dedicated Cloud, an organization admin can exclude PII when fetching audit logs.
- For Multi-tenant Cloud, the API endpoint always returns relevant fields for audit logs, including PII. This is not configurable.
Actions
This table describes possible actions that can be recorded by W&B, sorted alphabetically.
| Action | Definition |
|---|---|
artifact:create |
Artifact is created. |
artifact:delete |
Artifact is deleted. |
artifact:read |
Artifact is read. |
project:delete |
Project is deleted. |
project:read |
Project is read. |
report:read |
Report is read. 1 |
run:delete_many |
Batch of runs is deleted. |
run:delete |
Run is deleted. |
run:stop |
Run is stopped. |
run:undelete_many |
Batch of runs is restored from trash. |
run:update_many |
Batch of runs is updated. |
run:update |
Run is updated. |
sweep:create_agent |
Sweep agent is created. |
team:create_service_account |
Service account is created for the team. |
team:create |
Team is created. |
team:delete |
Team is deleted. |
team:invite_user |
User is invited to team. |
team:uninvite |
User or service account is uninvited from team. |
user:create_api_key |
API key for the user is created. 1 |
user:create |
User is created. 1 |
user:deactivate |
User is deactivated. 1 |
user:delete_api_key |
API key for the user is deleted. 1 |
user:initiate_login |
User initiates log in. 1 |
user:login |
User logs in. 1 |
user:logout |
User logs out. 1 |
user:permanently_delete |
User is permanently deleted. 1 |
user:reactivate |
User is reactivated. 1 |
user:read |
User profile is read. 1 |
user:update |
User is updated. 1 |
1: On Multi-tenant Cloud, audit logs are not collected for:
- Open or Public projects.
- The
report:readaction. Useractions which are not tied to a specific organization.
2 - Use Prometheus monitoring
Use Prometheus with W&B Server. Prometheus installs are exposed as a kubernetes ClusterIP service.
Follow the procedure below to access your Prometheus metrics endpoint (/metrics):
-
Connect to the cluster with Kubernetes CLI toolkit, kubectl. See kubernetes’ Accessing Clusters documentation for more information.
-
Find the internal address of the cluster with:
kubectl describe svc prometheus -
Start a shell session inside your container running in your Kubernetes cluster with
kubectl exec. Hit the endpoint at<internal address>/metrics.Copy the command below and execute it in your terminal and replace
<internal address>with your internal address:kubectl exec <internal address>/metrics
A test pod starts, which you can exec into just to access anything in the network:
kubectl run -it testpod --image=alpine bin/ash --restart=Never --rm
From there you can choose to keep access internal to the network or expose it yourself with a kubernetes nodeport service.
3 - Configure Slack alerts
Integrate W&B Server with Slack.
Create the Slack application
Follow the procedure below to create a Slack application.
-
Visit https://api.slack.com/apps and select Create an App.

-
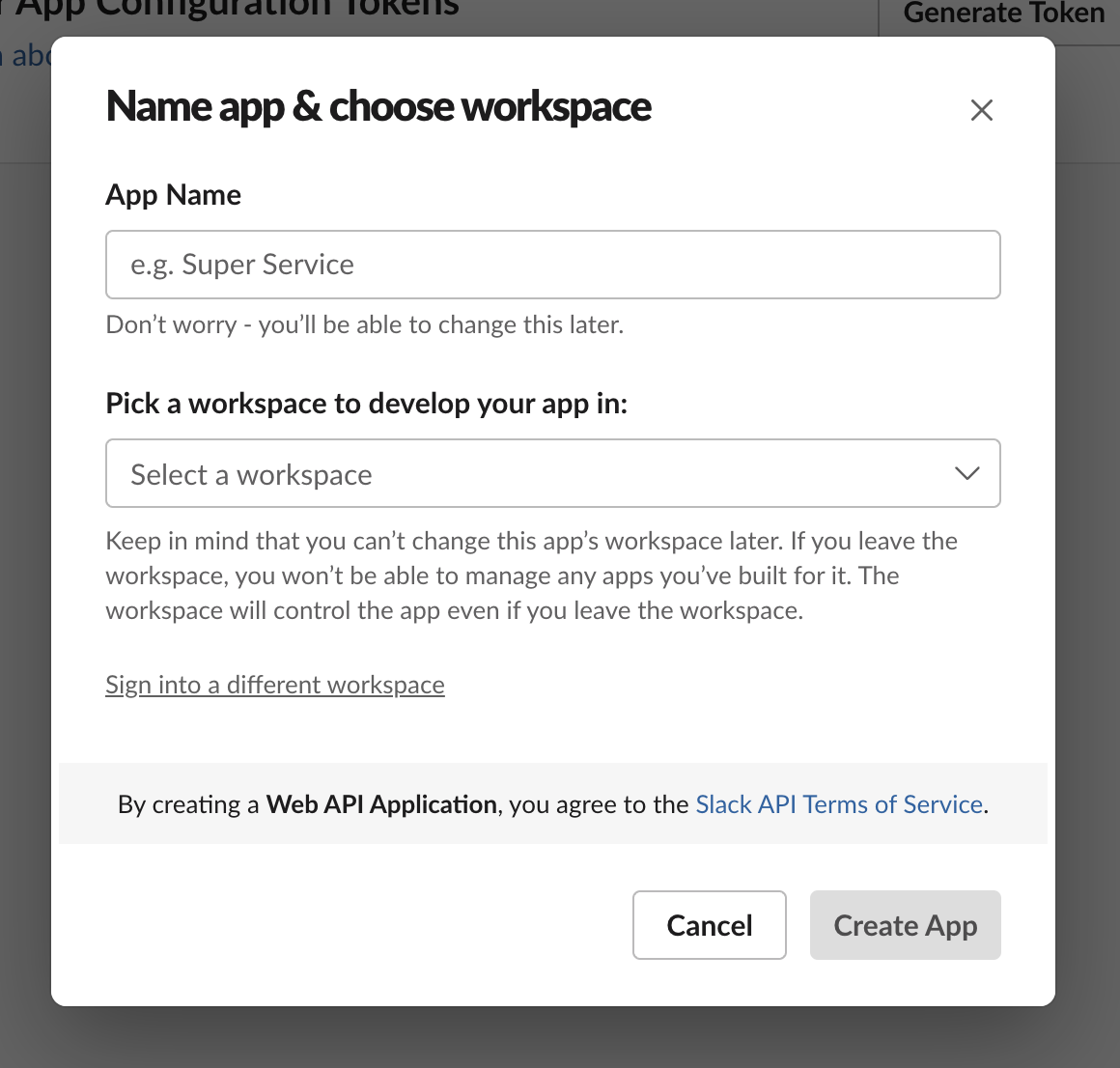
Provide a name for your app in the App Name field.
-
Select a Slack workspace where you want to develop your app in. Ensure that the Slack workspace you use is the same workspace you intend to use for alerts.
Configure the Slack application
-
On the left sidebar, select OAth & Permissions.
-
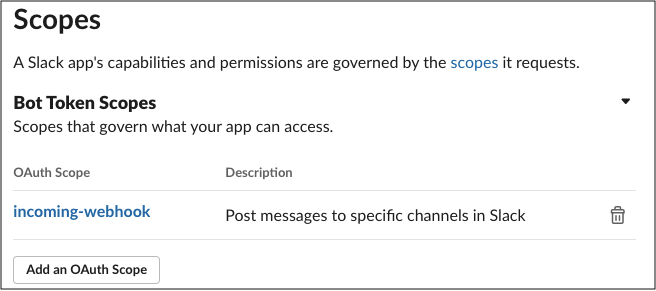
Within the Scopes section, provide the bot with the incoming_webhook scope. Scopes give your app permission to perform actions in your development workspace.
For more information about OAuth scopes for Bots, see the Understanding OAuth scopes for Bots tutorial in the Slack API documentation.
-
Configure the Redirect URL to point to your W&B installation. Use the same URL that your host URL is set to in your local system settings. You can specify multiple URLs if you have different DNS mappings to your instance.
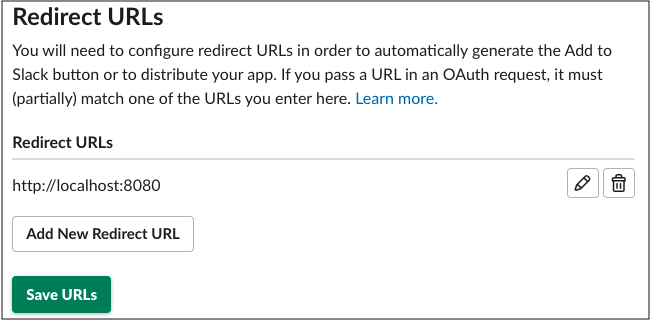
-
Select Save URLs.
-
You can optionally specify an IP range under Restrict API Token Usage, allow-list the IP or IP range of your W&B instances. Limiting the allowed IP address helps further secure your Slack application.
Register your Slack application with W&B
-
Navigate to the System Settings or System Console page of your W&B instance, depending on your deployment
-
Depending on the System page you are on follow one of the below options:
-
If you are in the System Console: go to Settings then to Notifications
-
If you are in the System Settings: toggle the Enable a custom Slack application to dispatch alerts to enable a custom Slack application

-
-
Supply your Slack client ID and Slack secret then click Save. Navigate to Basic Information in Settings to find your application’s client ID and secret.
-
Verify that everything is working by setting up a Slack integration in the W&B app.
4 - View organization activity
This page describes how to view activity in your W&B organization. Select your deployment type to continue.
View user status and activity
- Navigate to the Organization Dashboard at
https://<org-name>.io/org/dashboard/. Replace<org-name>with your organization name. The Users tab opens by default and lists every user in the organization. - To sort the list by user status, click the Last Active column header. Each user’s status is one of the following:
- Invite pending: An invitation was sent but not yet accepted.
- A timestamp: The user accepted the invitation and has signed in at least once. The timestamp indicates the most recent activity.
- Deactivated: An admin revoked the user’s access.
- No status: Indicated by a hyphen. The user was previously active but has not been active in the last six months.
- Hover over a user’s Last Active field to see the date the user was added and their total active days.
A user is active if they:
- sign in to W&B.
- open any page in the W&B App.
- log runs.
- use the SDK to track an experiment.
- interact with the W&B server in any way.
- Open the Members page. The table lists every user in your organization.
- Click the Last Active column header to sort by user status. Each user’s status is one of the following:
- A timestamp: The user has signed in at least once. The timestamp indicates the most recent activity.
- No status: Indicated by a hyphen. The user has not yet been active within the organization.
A user is active if they perform any auditable action scoped to the organization after May 8 2025. For a full list, see Actions in Audit logging.
View activity over time
Use the Activity tab to see how many users have been active during a given period.
- Open the Organization Dashboard (
https://<org-name>.io/org/dashboard/). - Click Activity.
- Review the following plots:
- Total active users: unique active users during the selected period (defaults to 3 months).
- Users active over time: fluctuation of active users over the period (defaults to 6 months). Hover over a point to see the exact count on that date.
To change the period, use the drop-down above a plot. Options are Last 30 days, Last 3 months, Last 6 months, Last 12 months, and All time.
Use the Activity Dashboard to view aggregate activity.
- Click your user icon in the upper-right corner of the W&B App.
- Under Account, click Users.
- Above the table of users, review the Activity Panel:
- Active user count: unique active users during the selected period (defaults to 3 months).
- Weekly active users: users active per week.
- Most active user: top-10 users ranked by active days and last-active date.
- To change the date range (7, 30, or 90 days; default is 30 days), click the date picker in the upper-right corner. All plots update automatically.
Export user details
From the Users tab you can download a CSV that lists each user’s details (user name, email address, last-active time, roles, and more).
- In the Users tab, click the … actions menu next to Invite new user.
- Click Export as CSV.
- In the Users tab, click the … actions menu in the upper-right corner.
- Select Export as CSV to download the file.
The CSV export uses the comma (,) as the separator, encloses strings in double quotes, and includes a header row that defines these columns:
"Name""Username""Last active""Role""Email""Teams""Status""Number of Reports""Number of Runs""Number of active days""Models Seat"